Imagine an internet in which economic power is more broadly distributed, so that more people can build and maintain small businesses online to make good livings. In this world, the behavioral advertising that has made the internet into a giant surveillance tool would be banned, so people could share more equally in the riches without surrendering their privacy.

(You can also find this episode on the Internet Archive and on YouTube.)
That’s the world Tim Wu envisions as he teaches and shapes policy on the revitalization of American antitrust law and the growing power of big tech platforms. He joins EFF’s Cindy Cohn and Jason Kelley to discuss using the law to counterbalance the market’s worst instincts, in order to create an internet focused more on improving people’s lives than on meaningless revenue generation.
In this episode you’ll learn about:
- Getting a better “deal” in trading some of your data for connectedness.
- Building corporate structures that do a better job of balancing the public good with private profits.
- Creating a healthier online ecosystem with corporate “quarantines” to prevent a handful of gigantic companies from dominating the entire internet.
- Nurturing actual innovation of products and services online, not just newer price models.
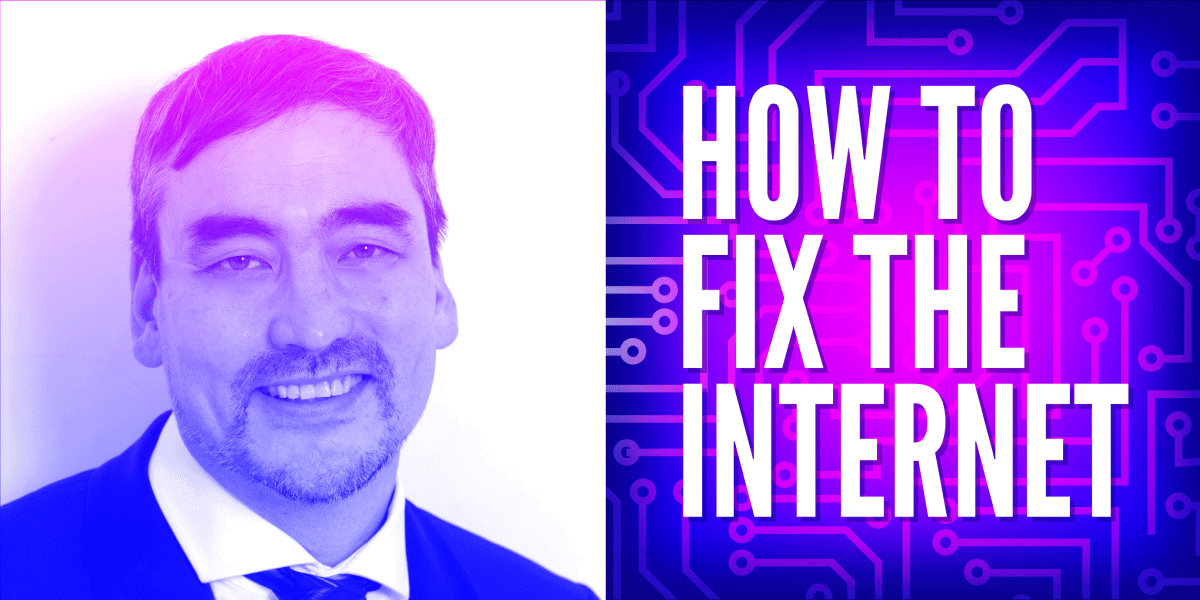
Timothy Wu is the Julius Silver Professor of Law, Science and Technology at Columbia Law School, where he has served on the faculty since 2006. First known for coining the term “net neutrality” in 2002, he served in President Joe Biden’s White House as special assistant to the President for technology and competition policy from 2021 to 2023; he also had worked on competition policy for the National Economic Council during the last year of President Barack Obama’s administration. Earlier, he worked in antitrust enforcement at the Federal Trade Commission and served as enforcement counsel in the New York Attorney General’s Office. His books include “The Curse of Bigness: Antitrust in the New Gilded Age” (2018), "The Attention Merchants: The Epic Scramble to Get Inside Our Heads” (2016), “The Master Switch: The Rise and Fall of Information Empires” (2010), and “Who Controls the Internet? Illusions of a Borderless World” (2006).
Resources:
- Columbia Law School: “How to Change 40 Years of Policy in 22 Months: Professor Wu in Washington" (Feb. 8. 2023)
- New York Times: “In Regulating A.I., We May Be Doing Too Much. And Too Little.” (Nov. 7, 2023)
- New York Times: “The Google Trial Is Going to Rewrite Our Future” (Sept. 18, 2023)
- CNBC: “Tech companies have exploited human tendencies to maintain their monopolies, says Columbia's Tim Wu” (Oct. 3, 2023)
What do you think of “How to Fix the Internet?” Share your feedback here.
Transcript
TIM WU
I think with advertising we need a better deal. So advertising is always a deal. You trade your attention and you trade probably some data, in exchange you get exposed to advertising and in exchange you get some kind of free product.
You know, that's the deal with television, that's been the deal for a long time with radio. But because it's sort of an invisible bargain, it's hard to make the bargain, and the price can be increased in ways that you don't necessarily notice. For example, we had one deal with Google in, let's say, around the year 2010 - if you go on Google now, it's an entirely different bargain.
It's as if there's been a massive inflation in these so-called free products. In terms of how much data has been taken, in terms of how much you're exposed to, how much ad load you get. It's as if sneakers went from 30 dollars to 1,000 dollars!
CINDY COHN
That's Tim Wu – author, law professor, White House advisor. He’s something of a swiss army knife for technology law and policy. He spent two years on the National Economic Council, working with the Biden administration as an advisor on competition and tech policy. He worked on antitrust legislation to try and check some of the country’s biggest corporations, especially, of course, the tech giants.
I’m Cindy Cohn - executive director of the Electronic Frontier Foundation.
JASON KELLEY
And I’m Jason Kelley - EFF’s Activism Director. This is our podcast, How to Fix the Internet. Our guest today is Tim Wu. His stint with the Biden administration was the second White House administration he advised. And in between, he ran for statewide office in New York. And that whole thing is just a sideline from his day job as a law professor at Columbia University. Plus, he coined the term net neutrality!
CINDY COHN
On top of that, Tim basically writes a book every few years that I read in order to tell me what's going to happen next in technology. And before that he's been a programmer and a more traditional lab based scientist. So he's kind of got it all.
TIM WU
Sounds like I'm a dilettante.
CINDY COHN
Well, I think you've got a lot of skills in a lot of different departments, and I think that in some ways, I've heard you call yourself a translator, and I think that that's really what all of that experience gives you as a superpower is the ability to kind of talk between these kinds of spaces in the rest of the world.
TIM WU
Well, I guess you could say that. I've always been inspired by Wilhelm Humboldt, who had this theory that in order to have a full life, you had to try to do a lot of different stuff. So somehow that factors into it somewhere.
CINDY COHN
That's wonderful. We want to talk about a lot of things in this conversation, but I kind of wanted to start off with the central story of the podcast, which is, what does the world look like if we get this right? You know, you and I have spent a lot of years talking about all the problems, trying to lift up obstacles and get rid of obstacles.
But if we reach this end state where we get a lot of these problems right, in Tim Wu's world, what, what does it look like? Like, what does your day look like? What do people's experience of technology look like?
TIM WU
I think it looks like a world in which economic power surrounding the internet and surrounding the platforms is very much more distributed. And, you know, what that means practically is it means a lot of people are able to make a good living, I guess, based on being a small producer or having a service based skill in a way that feels sustainable and where the sort of riches of the Internet are more broadly shared.
So that's less about what kind of things you click on or, you know, what kind of apps you use and more about, I guess, the economic structure surrounding the Internet, which I think, you know, um, I don't think I'm the only person who thinks this, you know, the structure could be fairer and could work for more people.
It does feel like the potential and, you know, we've all lived through that potential starting in the 90s of this kind of economically liberating force that would be the basis for a lot of people to make a decent living has seemed to turn into something more where a lot of money aggregates in a few places.
CINDY COHN
Yeah, I remember, people still talk about the long tail, right, as a way in which the digitization of materials created a revenue stream that's more than just, you know, the flavor of the week that a movie studio or a book publisher might want us to pay attention to on kind of the cultural side, right?
That there was space for this. And that also makes me think of a conversation we just had with the folks in the right to repair movement talking about like their world includes a place where there's mom and pop shops that will help you fix your devices all over the place. Like this is another way in which we have centralized economic power.
We've centralized power and if we decentralize this or, or, or spread it more broadly, uh, we're going to create a lot of jobs and opportunities for people, not just as users of technology, but as the people who help build and offer it to us.
TIM WU
I'm writing a new book, um, working title, Platform Capitalism, that has caused me to go back and look at the, you know, the early promise of the internet. And I went back and I was struck by a book, some of you may remember, called "An Army of Davids," by Glenn Reynolds the Instapundit.
Yeah, and he wrote a book and he said, you know, the future of the American economy is going to be all these kind of mom and pop sellers who, who take over everything – he wrote this about 2006 – and he says, you know, bloggers are already competing with news operations, small sellers on eBay are already competing with retail stores, and so on, journalists, so on down the line that, uh, you know, the age of the big, centralized Goliath is over and the little guys are going to rule the future.
Kind of dovetailed, I went back and read Yochai Benkler's early work about a production commons model and how, you know, there'll be a new node of production. Those books have not aged all that well. In fact, I think the book that wins is Blitzscaling. That somewhere along the line, instead of the internet favoring small business, small production, things went in the exact opposite direction.
And when I think about Yochai Benkler's idea of sort of production-based commons, you know, Waze was like that, the mapping program, until one day Waze was just bought by Google. So, I was just thinking about those as I was writing that chapter of the book.
CINDY COHN
Yeah, I think that's right. I think that identifying and, and you've done a lot of work on this, identify the way in which we started with this promise and we ended up in this other place can help us figure out, and Cory Doctorow, our colleague and friend has been doing a lot of work on this with choke point capitalism and other work that he's done for EFF and elsewhere.
And I also agree with him that, like, we don't really want to create the good old days. We want to create the good new days, right? Like, we want to experience the benefits of an Internet post-1990s, but also have those, those riches decentralized or shared a little more broadly, or a lot more broadly, honestly.
TIM WU
Yeah, I think that's right, and so I think part of what I'm saying, you know, what would fix the internet, or what would make it something that people feel excited about. You know, I think people are always excited about apps and videos, but also people are excited about their livelihood and making money.
And if we can figure out the kind of structure that makes capitalism more distributed surrounding platforms, you know, it's not abandoning the idea of you have to have a good site or a product or something to, to gain customers. It's not a total surrender of that idea, but a return to that idea working for more people.
CINDY COHN
I mean, one of the things that you taught me in the early days is how kind of ‘twas ever so, right? If you think about radio or broadcast medium or other previous mediums, they kind of started out with this promise of a broader impact and broader empowerment and, and didn't end up that way as much as well.
And I know that's something you've thought about a lot.
TIM WU
Yeah, the first book I wrote by myself, The Master Switch, had that theme and at the time when I wrote it, um, I wrote a lot of it in the, ‘09, ‘08, ‘07 kind of period, and I think at that point I had more optimism that the internet could hold out, that it wouldn't be subject to the sort of monopolizing tendencies that had taken over the radio, which originally was thousands of radio stations, or the telephone system – which started as this ‘go west young man and start your own telephone company’ kind of technology – film industry and and many others. I was firmly of the view that things would be different. Um, I think I thought that, uh, because of the CCP IP protocol, because of the platforms like HTML that were, you know, the center of the web, because of net neutrality, lasting influence. But frankly, I was wrong. I was wrong, at least when I was writing the book.
JASON KELLEY
As you've been talking about the sort of almost inevitable funneling of the power that these technologies have into a single or, or a few small platforms or companies, I wonder what you think about newer ideas around decentralization that have sort of started over the last few years, in particular with platforms like Mastodon or something like that, these kinds of APIs or protocols, not platforms, that idea. Do you see any promise in that sort of thing? Because we see some, but I'm wondering what you think.
TIM WU
I do see some promise. I think that In some ways, it's a long overdue effort. I mean, it's not the first. I can't say it's the first. Um, and part of me wishes that we had been, you know, the idealistic people. Even the idealistic people at some of these companies, such as they were, had been a bit more careful about their design in the first place.
You know, I guess what I would hope … the problem with Mastodon on some of these is they're trying to compete with entities that already are operating with all the full benefits of scale and which are already tied to sort of a Delaware private corporate model. Uh, now this is a little bit, I'm not saying that hindsight is 20/20, but when I think about the major platforms and entities the early 21st century, it's really only Wikipedia that got it right in my view by structurally insulating themselves from certain forces and temptations.
So I guess what I'm trying to say is that, uh, part of me wishes we'd done more of this earlier. I do think there's hope in them. I think it's very challenging in current economics to succeed. And sometimes you'd have to wonder if you go in a different, you know, that it might be, I don't want to say impossible, very challenging when you're competing with existing structures. And if you're starting something new, you should start it right.
That said, AI started in a way structurally different and we've seen how that's gone recently.
CINDY COHN
Oh, say more, say more!
JASON KELLEY
Yeah. Yeah. Keep, keep talking about AI.
CINDY COHN
I'm very curious about your thinking about that.
TIM WU
Well, you know, I said that, The Holy Roman Empire was neither holy, nor Roman, nor an empire. And OpenAI is now no longer open, nor non-profit, nor anything else. You know, it's kind of, uh, been extraordinary that the circuit breakers they tried to install have just been blown straight through. Um, and I think there's been a lot of negative coverage of the board. Um, because, you know, the business press is kind of narrow on these topics. But, um, you know, OpenAI, I guess, at some point, tried to structure itself more carefully and, um, and, uh, you know, now the board is run by people whose main experience has been, um, uh, taking good organizations and making them worse, like Quora, so, yeah, I, I, that is not exactly an inspiring story, uh, I guess of OpenAI in the sense of it's trying to structure itself a little differently and, and it, uh, failing to hold.
CINDY COHN
I mean, I think Mozilla has managed to have a structure that has a, you know, kind of complicated for profit/not-for-profit strategy that has worked a little better, but II hear you. I think that if you do a power analysis, right, you know, a nonprofit is going to have a very hard time up against all the money in the world.
And I think that that seems to be what happened for OpenAI. Uh, once all the money in the world showed up, it was pretty hard to, uh, actually impossible for the public interest nonprofit side to hold sway.
TIM WU
When I think about it over and over, I think engineers and the people who set up these, uh, structures have been repeatedly very naive about, um, the power of their own good intentions. And I agree. Mozilla is a good example. Wikipedia is a good example. Google, I remember when they IPO'd, they had some set up, and they said, ‘We're not going to be an ordinary company,’ or something like that. And they sort of had preferred stock for some of the owners. You know, Google is still in some ways an impressive company, but it's hard to differentiate them from any other slightly money grubbing, non-innovative colossus, um, of the kind they were determined not to become.
And, you know, there was this like, well, it's not going to be us, because we're different. You know, we're young and idealistic, and why would we want to become, I don't know, like Xerox or IBM, but like all of us, you begin by saying, I'm never going to become like my parents, and then next thing you know, you're yelling at your kids or whatever.
CINDY COHN
Yeah, it's, it's the, you know, meet the new boss the same as the old boss, right? When we, what we were hoping was that we would be free of some of the old bosses and have a different way to approach, but, but the forces are pretty powerful that stick people back in line, I think.
TIM WU
And some of the old structures, you know, look a little better. Like, I'm not going to say newspapers are perfect, but a structure like the New York Times structure, for example, basically is better than Google's. And I just think there was this sense that, Well, we can solve that problem with code and good vibes. And that turned out to be the great mistake.
CINDY COHN
One of the conversations that you and I have had over the years is kind of the role of regulation on, on the internet. I think the fight about whether to regulate or not to regulate the Internet was always a little beside the point. The question is how. And I'm wondering what you're thinking now. You've been in the government a couple times. You've tried to push some things that were pretty regulatory. How are you thinking now about something like a centralized regulatory agency or another approach to, you know, regulating the Internet?
TIM WU
Yeah, I, you know, I continue to have mixed feelings about something like the central internet commission, mostly for some of the reasons you said, but on the other hand, sometimes, if I want to achieve what I mentioned, which is the idea of platforms that are an input into a lot of people being able to operate on top of them and run businesses-like, you know, at times, the roads have been, or the electric system, or the phone network, um, it's hard to get away from the idea of having some hard rules, sometimes I think my sort of platonic form of, of government regulation or rules was the 1956 AT&T consent decree, which, for those who are not as deep in those weeds as I am, told AT&T that it could do nothing but telecom, and therefore not do computing and also force them to license every single one of their patents for free. And the impact of that was more than one - one is because they were out of computing. They were not able to dominate it and you had companies then new to computing like IBM and others that got into that space and developed the American computing industry completely separate from AT&T.
And you also ended up, semiconductor companies start that time with the transistor patent and other patents they used for free. So you know, I don't know exactly how you achieve that, but I'm drawn to basically keeping the main platforms in their lane. I would like there to be more competition.
The antitrust side of me would love it. And I think that in some areas we are starting to have it, like in social media, for better or for worse. But maybe for some of the more basic fundamentals, online markets and, you know, as much competition as we can get – but some rule to stay out of other businesses, some rule to stop eating the ecosystem. I do think we need some kind of structural separation rules. Who runs those is a little bit of a harder question.
CINDY COHN
Yeah, we're not opposed to structural separation at EFF. I think we, we think a lot more about interoperability to start with as a way to, you know, help people have other choices, but we haven't been opposed to structural separation, and I think there are situations in which it might make a lot of good sense, especially, you know, in the context of mergers, right?
Where the company has actually swallowed another company that did another thing. That's, kind of the low hanging fruit, and EFF has participated a lot in commenting on potential mergers.
TIM WU
I'm not opposed the idea of pushing interoperability. I think that it's based on the experience of the last 100 years. It is a tricky thing to get right. I'm not saying it's impossible. We do have examples: Phone network, in the early 20th century, and interconnection was relatively successful. And right now, you know, when you change between, let's say, T-Mobile and Verizon, there's only three left, but you get to take your phone number with you, which is a form of interoperability.
But it has the risk of being something you put a lot of effort into and it not necessarily working that well in terms of actually stimulating competition, particularly because of the problem of sabotage, as we saw in the ‘96 Act. So it's actually not about the theory, it's about the practice, the legal engineering of it. Can you find the right thing where you've got kind of a cut point where you could have a good interoperability scheme?
JASON KELLEY
Let’s take a quick moment to say thank you to our sponsor. “How to Fix the Internet” is supported by The Alfred P. Sloan Foundation’s Program in Public Understanding of Science and Technology. Enriching people’s lives through a keener appreciation of our increasingly technological world and portraying the complex humanity of scientists, engineers, and mathematicians.
And now back to our conversation with Tim Wu. I was intrigued by what he said about keeping platforms in their lane. I wanted to hear him speak more about how that relates to antitrust – is that spreading into other ecosystems what sets his antitrust alarm bells off? How does he think about that?
TIM WU
I guess the phrase I might use is quarantine, is you want to quarantine businesses, I guess, from others. And it's less of a traditional antitrust kind of remedy, although it, obviously, in the ‘56 consent decree, which was out of an antitrust suit against AT&T, it can be a remedy.
And the basic idea of it is, it's explicitly distributional in its ideas. It wants more players in the ecosystem, in the economy. It's almost like an ecosystem promoting a device, which is you say, okay, you know, you are the unquestioned master of this particular area of commerce. Maybe we're talking about Amazon and it's online shopping and other forms of e-commerce, or Google and search.
We're not going to give up on the hope of competition, but we think that in terms of having a more distributed economy where more people have their say, um, almost in the way that you might insulate the college students from the elementary school students or something. We're going to give other, you know, room for other people to develop their own industries in these side markets. Now, you know, there's resistance say, well, okay, but Google is going to do a better job in, uh, I don't know, shopping or something, you know, they might do a good job. They might not, but you know, they've got their returns and they're always going to be an advantage as a platform owner and also as a monopoly owner of having the ability to cross-subsidize and the ability to help themselves.
So I think you get healthier ecosystems with quarantines. That's basically my instinct. And, you know, we do quarantines either legally or de facto all the time. As I said, the phone network has long been barred from being involved in a lot of businesses. Banking is kept out of a lot of businesses because of obvious problems of corruption. The electric network, I guess they could make toasters if they want, but it was never set up to allow them to dominate the appliance markets.
And, you know, if they did dominate the appliance markets, I think it would be a much poorer world, a lot less interesting innovation, and frankly, a lot less wealth for everyone. So, yeah, I have strong feelings. It's more of my net neutrality side that drives this thinking than my antitrust side, I’ll put it that way.
JASON KELLEY
You specifically worked in both the Obama and Biden administration sort of on these issues. I'm wondering if your thinking on this has changed. In experiencing those things from from the sort of White House perspective and also just how different those two, sort of, experiences were, obviously the moments are different in time and and and everything like that, but they're not so far apart – maybe light years in terms of technology, but what was your sort of experience between those two, and how do you think we're doing now on this issue?
TIM WU
I want to go back to a slightly earlier time in government, not the Obama, actually it was the Obama administration, but my first job in the, okay, sorry, my third job in the federal government, uh, I guess I'm a, one of these recidivists or something, was at the Federal Trade Commission.
CINDY COHN
Oh yeah, I remember.
TIM WU
Taking the first hard look at big tech and, in fact, we're investigating Google for the first time for antitrust possible offenses, and we also did the first privacy remedy on Facebook, which I will concede was a complete and absolute failure of government, one of the weakest remedies, I think. We did that right before Cambridge Analytica. And obviously had no effect on Facebook's conduct at all. So, one of the failed remedies. I think that when I think back about that period, the main difference was that the tech platforms were different in a lot of ways.
I believe that, uh, monopolies and big companies have, have a life cycle. And they were relatively early in that life cycle, maybe even in a golden age. A company like Amazon seemed to be making life possible for a lot of sellers. Google was still in its early phase and didn't have a huge number of verticals. Still had limited advertising. Most searches still didn't turn up that many ads.
You know, they were in a different stage of their life. And they also still felt somewhat, they were still already big companies. They still felt relatively in some sense, vulnerable to even more powerful economic forces. So they hadn't sort of reached that maturity. You know, 10 years later, I think the life cycle has turned. I think companies have largely abandoned innovation in their core products and turned to defense and trying to improve – most of their innovations are attempting to raise more revenue and supposed to make the product better. Uh, kind of reminds me of the airline industry, which stopped innovating somewhere in the seventies and started making, trying to innovate in, um, terms of price structures and seats being smaller, that kind of thing.
You know, there's, you reach this end point, I think the airlines are the end point where you take a high tech industry at one point and just completely give up on anything other than trying to innovate in terms of your pricing models.
CINDY COHN
Yeah, I mean, I, you know, our, our, we, Cory keeps coming up, but of course Cory calls it the “enshittification” of, uh, of services, and I think that is, uh, in typical Corrie way captures, this stage of the process.
TIM WU
Yeah, I just to speak more broadly. I you know, I think there's a lot of faith and belief that the, uh, company like Google, you know, in its heart meant well, and I do still think the people working there mean well, but I feel that, you know, the structure they set up, which requires showing increasing revenue and profit every quarter began to catch up with it much more and we’re at a much later stage of the process.
CINDY COHN
Yep.
TIM WU
Or the life cycle. I guess I'd put it.
CINDY COHN
And then for you, kind of coming in as a government actor on this, like, what did that mean in terms of, like, was it, I'm assuming, I kind of want to finish the sentence for you. And that, you know, that meant it was harder to get them to do the right thing. It meant that their defenses were better against trying to do the right thing.
Like how did that impact the governmental interventions that you were trying to help make happen?
TIM WU
I think it was both. I think there was both, in terms of government action, a sense that the record was very different. The Google story in 2012 is very different than 2023. And the main difference is in 2023 Google is paying out 26.3 billion a year to other companies to keep its search engine where it is, and arguably to split the market with Apple.
You know, there wasn't that kind of record back in 2012. Maybe we still should have acted, but there wasn't that much money being so obviously spent on pure defensive monopoly. But also people were less willing. They thought the companies were great. They overall, I mean, there's a broader ideological change that people still felt, many people from the Clinton administration felt the government was the problem. Private industry was the solution. Had kind of a sort of magical thinking about the ability of this industry to be different in some fundamental way.
So the chair of the FCC wasn't willing to pull the trigger. The economists all said it was a terrible idea. You know, they failed to block over a thousand mergers that big tech did during that period, which it's, I think, very low odds that none of those thousands were anti-competitive or in the aggregate that maybe, you know, that was a way of building up market power.
Um, it did enrich a lot of small company people, but I, I think people at companies like Waze really regret selling out and, you know, end up not really building anything of their own but becoming a tiny sub-post of the Google empire.
CINDY COHN
Yeah, the “acquihire” thing is very central now and what I hear from people in the industry is that like, if that's not your strategy to get acquired by one of the ones, it's very hard to get funded, right? It feeds back into the VC and how you get funded to get something built.
If it's not something that one of the big guys is going to buy, you're going to have a hard time building it and you're going to have a hard time getting the support to get to the place where you might actually even be able to compete with them.
TIM WU
And I think sometimes people forget we had different models. You know, some of your listeners might forget that, you know, in the ‘70s, ‘80s, and ‘90s, and early 2000s, people did build companies not just to be bought...
CINDY COHN
Right.
TIM WU
...but to build fortunes, or because they thought it was a good company. I mean, the people who built Sun, or Apple, or, you know, Microsoft, they weren't saying, well, I hope I'm gonna be bought by IBM one day. And they made real fortunes. I mean, look, being acquired, you can obviously become a very wealthy person, but you don't become a person of significance. You can go fund a charity or something, but you haven't really done something with your life.
CINDY COHN
I'm going to flip it around again. And so we get to the place where the Tim Wu vision that the power is spread more broadly. We've got lots of little businesses all around. We've got many choices for consumers. What else, what else do you see in this world? Like what role does the advertising business model play in this kind of a better future. That's just one example there of many, that we could give.
TIM WU
Yeah, no, I like your vision of a different future. I think, uh, just like focus on it goes back to the sense of opportunity and, you know, you could have a life where you run a small business that's on the internet that is a respectable business and you're neither a billionaire nor you're impoverished, but you know, you just had to have your own business the way people have, like, in New York or used to run like stores and in other parts of the country, and in that world, I mean, in my ideal world, there is advertising, but advertising is primarily informational, if that makes sense.
It provides useful information. And it's a long way to go between here and there, but where, um, you know, it's not the default business model for informational sources such that it, it has much less corrupting effects. Um, you know, I think that advertising obviously everyone's business model is going to affect them, but advertising has some of the more, corrupting business models around.
So, in my ideal world, we would not, it's not that advertising will go away, people want information, but we'd strike a better bargain. Exactly how you do that. I guess more competition helps, you know, lower advertising, um, sites you might frequent, better privacy protecting sites, but, you know, also passing privacy legislation might help too.
CINDY COHN
I think that’s right, I think EFF has taken a position that we think we should ban behavioral ads. That's a pretty strong position for us and not what we normally do, um, to, to say, well, we need to ban something. But also that we need, of course, comprehensive privacy law, which is, you know, kind of underlines so many of the harms that we're seeing online right now is this, this lack of a baseline privacy protection.
I don't know if you see it the same way, but it's certainly it seems to be the through line for a lot of harms that are coming up as things people are concerned about. Yeah.
TIM WU
I mean, absolutely, and I, you know, don't want to give EFF advice on their views, but I would say that I think it's wise to see the totally unregulated collection of data from, you know, millions, if not billions of people as a source of so many of the problems that we have.
It drives unhealthy business models, it leads to real-world consequences, in terms of identity theft and, and so many others, but I think I, I'd focus first on what, yeah, the kind of behavior that encourages the kind of business model is encourages, which are ones that just don't in the aggregate, feel very good for the businesses or for, for us in particular.
So yeah, my first priority legislatively, I think if I were acting at this moment would be starting right there with, um, a privacy law that is not just something that gives supposed user rights to take a look at the data that's collected, but that meaningfully stops the collection of data. And I think we'll all just shrug our shoulders and say, oh, we're better off without that. Yes, it supported some, but we will still have some of the things – it's not as if we didn't have friends before Facebook.
It's not as if we didn't have video content before YouTube, you know, these things will survive with less without behavioral advertising. I think your stance on this is entirely, uh, correct.
CINDY COHN
Great. Thank you, I always love it when Tim agrees with me and you know, it pains me when we disagree, but one of the things I know is that you are one of the people who was inspired by Larry Lessig and we cite Larry a lot on the show because we like to think about things or organize them in terms of the four levels of, um, You know, digital regulation, you know, laws, norms, markets, and code as four ways that we could control things online. And I know you've been focusing a lot on laws lately and markets as well.
How do you think about, you know, these four levers and where we are and, and how we should be deploying them?
TIM WU
Good question. I regard Larry as a prophet. He was my mentor in law school, and in fact, he is responsible for most of my life direction. Larry saw that there was a force arising through code that already was somewhat, in that time, 90s, early 2000s, not particularly subject to any kind of accountability, and he saw that it could take forms that might not be consistent with the kind of liberties you would like to have or expect and he was right about that.
You know, you can say whatever you want about law or government and there are many examples of terrible government, but at least the United States Constitution we think well, there is this problem called tyranny and we need to do something about it.
There's no real equivalent for the development of abusive technologies unless you get government to do something about it and government hasn't done much about it. You know, I think the interactions are what interests me about the four forces. So if we agree that code has a certain kind of sovereignty over our lives in many ways and most of us on a day-to-day basis are probably more affected by the code of the devices we use than by the laws we operate under.
And the question is, what controls code? And the two main contenders are the market and law. And right now the winner by far is just the market, which has led codemakers in directions that even they find kind of unfortunate and disgraceful.
I don't remember who had that quote, but it was some Facebook engineer that said the greatest minds of our generation are writing code to try to have people click on random ads, and we have sort of wasted a generation of talent on meaningless revenue generation when they could be building things that make people's lives better.
So, you know, the answer is not easy is to use law to counter the market. And that's where I think we are with Larry's four factors.
CINDY COHN
Yeah, I think that that's right, and I agree that it's a little ro-sham-bo, right, that you can control code with laws and, and markets and you can control markets with code, which is kind of where interoperability comes in sometimes and laws and you know, norms play a role in kind of a slightly different whammy role in all of these things, but I do think that those interactions are really important and we've, again, I've always thought it was a somewhat phony conversation about, you know, "to regulate or not to regulate, that is the question" because that's not actually particularly useful in terms of thinking about things because we were embedded in a set of laws. It's just the ones we pay attention to and the ones that we might not notice, but I do think we're in a time when we have to think a lot harder about how to make laws that will be flexible enough to empower people and empower competition and not lock in the winners of today's markets. And we spend a lot of time thinking about that issue.
TIM WU
Well, let me say this much. This might sound a little contradictory in my life story, but I'm not actually a fan of big government, certainly not overly prescriptive government. Having been in government, I see government's limits, and they are real. But I do think the people together are powerful.
I think laws can be powerful, but what they most usefully do is balance out the market. You know what I'm saying? And create different incentives or different forces against it. I think trying to have government decide exactly how tech should run is usually a terrible idea. But to cut off incentives – you talked about behavioral advertising. So let's say you ban behavioral advertising just the way we ban child labor or something. You know, you can live without it. And, yeah, maybe we're less productive because we don't let 12 year olds work in factories. There's a marginal loss of revenue, but I frankly think it's worth it.
And, you know, and some of the other practices that have shown up are in some ways the equivalent. And we can live without them. And that's the, you know, it's sort of easy to say. we should ban child labor. But when you look for those kind of practices, that's where we need law to be active.
JASON KELLEY
Well, Cindy, I came away from that with a reading list. I'm sure a lot of people are familiar with those authors and those books, but I am going to have to catch up. I think we'll put some of them, maybe all the books, in the, in the show notes so that people who are wondering can, can catch up on their end.
You, as someone who's already read all those books, probably have different takeaways from this conversation than me.
CINDY COHN
You know what I really, I really like how Tim thinks he's, you know, he comes out of this, especially most recently from an economics perspective. So his future is really an economics one.
It's about an internet that has lots of spaces for people to make a reasonable living as opposed to the few people make a killing, or sell their companies to the big tech giants. And I think that that vision dovetails a lot with a lot of the people that we've talked. to on this show that, you know, in some ways we've got to think about how do we redistribute the internet and that includes redistributing the economic benefits.
JASON KELLEY
Yeah. And thinking about, you know, something you've said many times, which is this idea of rather than going backwards to the internet we used to have, or the world we used to have, we're really trying to build a better world with the one we do have.
So another thing he did mention that I really pulled away from this conversation was when antitrust makes sense. And that sort of idea of, well, what do you do when companies start spreading into other ecosystems? That's when you really have to start thinking about the problems that they're creating for competition.
And I think the word he used was quarantine. Is that right?
CINDY COHN
Yeah I love that image.
JASON KELLEY
Yeah, that was just a helpful, I think, way for people to think about how antitrust can work. And that was something that I'll take away from this probably forever.
CINDY COHN
Yeah, I also liked his vision of what kind of deal we have with a lot of these free tools or AKA free tools, which is, you know, at one time when we signed up for, you know, a Gmail account, it's, you know, the, the deal was that it was going to look at what you searched on and what you wrote and then place you ads based on the context and what you did.
And now that deal is much, much worse. And I think he, he's right to likening that to something that, you know, has secretly gotten much more expensive for us, that the deal for us as consumers has gotten worse and worse. And I really like that framing because again, it kind of translates out from the issues that where we live, which is, you know, privacy and free speech and fairness and turns it into something that is actually kind of an economic framing of some of the same points.
I think that the kind of upshot of Tim and, and honestly, some of the other people we've talked to is this idea of ‘blitzscaling’, um, and growing gigantic platforms is really at the heart of a lot of the problems that we're seeing in free speech and in privacy and also in economic fairness. And I think that's a point that Tim makes very well.
I think that from, you know, The Attention Merchants, The Curse of Bigness, Tim has been writing in this space for a while, and he, what I appreciate is Tim is really a person, um, who came up in the Internet, he understands the Internet, he understands a lot of the values, and so he's, he's not writing as an outsider throwing rocks as much as an insider who is kind of dismayed at how things have gone and looking to try to unpack all of the problems. And I think his observation, which is shared by a lot of people, is that a lot of the problems that we're seeing inside tech are also problems we're seeing outside tech. It's just that tech is new enough that they really took over pretty fast.
But I think that it's important for us to both recognize the problems inside tech and it doesn't let tech off the hook. To note that these are broader societal problems, but it may help us in thinking about how we get out of them.
JASON KELLEY
Thanks for joining us for this episode of How to Fix the Internet. If you have feedback or suggestions, we'd love to hear from you. Visit EFF. org slash podcast and click on listener feedback. While you're there, you can become a member, donate, maybe pick up some merch and just see what's happening in digital rights this week and every week.
We’ve got a newsletter, EFFector, as well as social media accounts on many, many, many platforms you can follow
This podcast is licensed Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International, and includes music licensed Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported by their creators.
In this episode you heard Perspectives *** by J.Lang featuring Sackjo22 and Admiral Bob, and Warm Vacuum Tube by Admiral Bob featuring starfrosch.
You can find links to their music in our episode notes, or on our website at eff.org/podcast.
Our theme music is by Nat Keefe of BeatMower with Reed Mathis
How to Fix the Internet is supported by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation's program in public understanding of science and technology.
We’ll talk to you again soon.
I’m Jason Kelley
CINDY COHN
And I’m Cindy Cohn.